Huntington’s disease is a rare but serious genetic disorder that affects the brain and nervous system. It is passed down from one generation to another, and once a person inherits the faulty gene, they are very likely to develop the disease. Huntington’s disease causes gradual breakdown of nerve cells in the brain, which impacts movement, emotions, and thinking abilities. Over time, it changes the way a person lives, making it important to understand the condition, its causes, and how it can be managed.
What is Huntington’s Disease?
Huntington’s disease is a progressive disorder, which means symptoms get worse over time. It usually starts in adulthood, most often between the ages of 30 and 50. In rare cases, it can also begin during childhood or teenage years, which is known as juvenile Huntington’s disease. Because it directly affects the brain, the disease can impact how a person controls their body, how they feel emotionally, and how they process information.
Causes of Huntington’s Disease
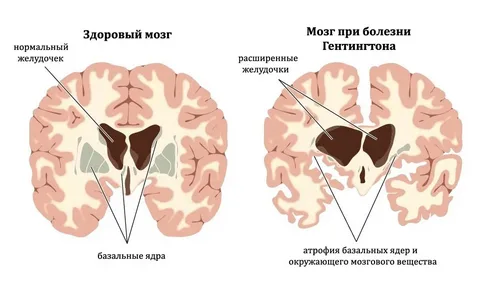
The main cause of Huntington’s disease is a genetic mutation. A person needs only one copy of the faulty gene from either parent to develop the disease. If one parent has Huntington’s disease, each child has a 50 percent chance of inheriting it. The gene involved is responsible for making a protein called huntingtin. When the gene mutates, it produces a harmful form of this protein that damages brain cells, leading to the symptoms of the disease.
Common Symptoms
Huntington’s disease shows itself in three main areas: movement, emotions, and thinking.
-
Movement problems include involuntary jerking, muscle stiffness, difficulty with balance, and trouble with speech or swallowing.
-
Emotional changes may involve depression, irritability, mood swings, or lack of motivation.
-
Cognitive symptoms include difficulty organizing tasks, poor concentration, and problems with decision-making.
At first, symptoms may be mild, but they gradually become more noticeable. Over time, everyday activities such as walking, talking, or eating may become difficult, and the person may need full-time care.
Juvenile Huntington’s Disease
When Huntington’s disease begins in children or teenagers, it progresses faster than in adults. Symptoms in young people may include difficulty learning, behavior problems, seizures, or a rapid decline in physical abilities. Although rare, juvenile Huntington’s disease can be especially challenging for families, as it requires special care and support.
Diagnosis
Doctors use a combination of medical history, neurological exams, and genetic testing to diagnose Huntington’s disease. Genetic testing can confirm whether a person has the faulty gene even before symptoms appear. However, because the disease is life-changing, many people choose carefully before deciding to take the test. Brain scans and other medical evaluations may also help doctors track the progression of the disease.
Treatment and Management
There is currently no cure for Huntington’s disease. However, treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Medications can help control movement problems and mood changes.
-
Physical therapy may improve strength, balance, and flexibility.
-
Speech therapy can help with communication and swallowing difficulties.
-
Psychological support provides emotional care for both patients and families.
While treatment cannot stop the disease from progressing, it can make daily life more manageable and provide comfort.
Impact on Families
Because Huntington’s disease is inherited, it often affects entire families. The emotional impact of knowing the condition may pass from parent to child can be heavy. Families may struggle with feelings of fear, guilt, or sadness. Support groups and counseling play an important role in helping families cope with these challenges. Sharing experiences with others who face the same struggles can reduce feelings of isolation and bring comfort.
Ongoing Research
Scientists around the world are working to better understand Huntington’s disease. Research is focused on finding ways to slow or stop the progression of the disease. Studies on gene therapy, new medications, and advanced treatment methods bring hope for the future. Clinical trials are also underway to test new approaches, giving patients and families optimism that effective treatments may be available one day.
Living with Huntington’s Disease
Even though Huntington’s disease is a difficult condition, many patients and families learn to adapt and find ways to live meaningfully. Building a supportive environment, maintaining healthy habits, and accessing medical care are important steps. Awareness about the disease also helps reduce stigma and promotes compassion for those affected.
Conclusion
Huntington’s disease is a genetic disorder that deeply impacts individuals and families. It causes gradual changes in movement, emotions, and thinking, making life challenging over time. While there is no cure yet, treatments and therapies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Families facing Huntington’s disease often show great resilience, and ongoing research continues to offer hope for future solutions. By learning more about this condition, society can better support those living with it and work toward finding a cure.












Comments are closed